Mass and Inertia
Mass and Inertia: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Inertia of Motion, Inertia of Rest, Descending by a Parachute & Terminal Velocity of an Object etc.
Important Questions on Mass and Inertia
How Stokes law helps a man coming down with the help of parachute?
What is inertia of rest? Give an example.
When balanced forces act on a body, the body :
When an unbalanced force acts on a vehicle, which of these quantities changes?
Rotational motion is impossible without an external force.
At the start of motion, an object under free fall will have :
A body is said to be in free fall, when only the _____ force acts on it.
The motion of an object where gravity is the only force acting upon it is known as
Assertion : Both the string and have equal tensile strength. If the lower string is pulled gradually then the upper string is more likely to break, but if the lower string is pulled with a jerk, then the lower string is more likely to break.
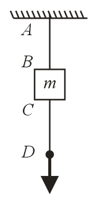
Reason : Due to the property of inertia the position of the block doesn't change suddenly. However its position can charge gradually.
Two objects of different masses falling freely near the surface of moon would
If all the forces acting on an object are balanced then what will be the magnitude of the net force?
(Choose from here: Non-zero/Zero/Can be any value)
Inertia is that property of a body. Which is correct about definition of inertia?
Name the property of matter which forms the basis of Newton’s first law of motion.
On a normal day if you drop a feather and a rubber ball together from a height, then the rubber ball reaches the surface of the earth first because of :
A ball is thrown up with an initial speed of . How high does it travel?
In figure a 100kg uniform log hangs by two steel wires A and B, both the area of cross-section . Initially, wire A was 2.50m long and 2.00mm shorter than wire B. The log is now horizontal. The Young's modulus of steel is
( and are the distances measured from the centre of log).
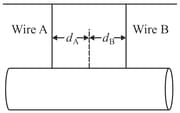
The extension produced in wire A is:
Which motion does not require force to maintain its motion?
